Phishing
What is phishing?
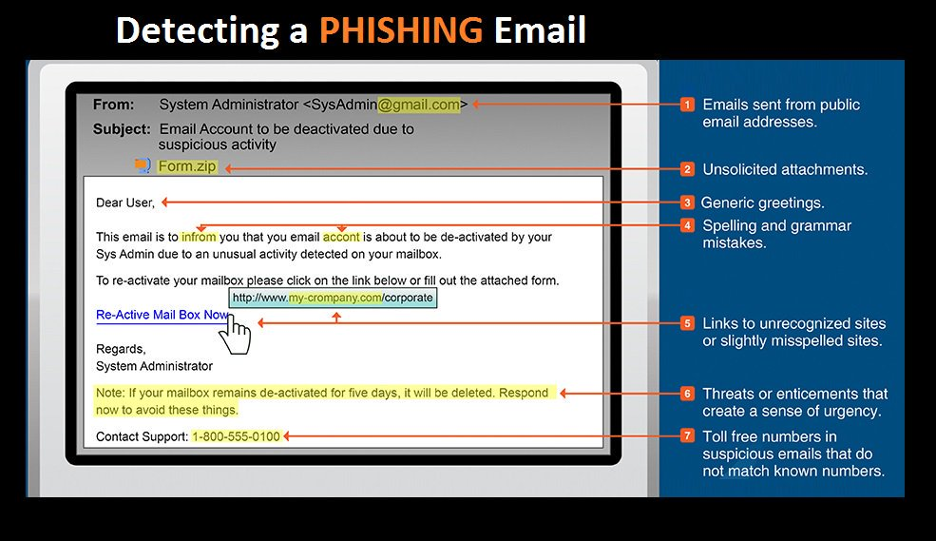
Phishing is a form of attack that depends on tricking or fooling a victim into doing what the attacker wants. The attack begins with the attacker sending a message to the victim. It is this technique of using a message as bait to lure the victim that gives the attack its name.
The attack is a success if the victim responds to the request. For instance, the victim may click a link or open an attachment that triggers some kind of threat. Other examples, the victim could respond to the attacker's message, or they could simply stay on the phone and speak with the caller.
In the case of communication between attacker and victim, the attacker will attempt to manipulate the victim using social norms and expectations to convince them. Some examples are when an attacker:
- Asks the victim to do a quick errand that they can't do.
- Calls where the attacker asks for help to appease their horrible boss, relying on the victim to help to avoid trouble.
- Informs the victim about a (fake) issue with their account and offers to help fix it.
Did you know that 93% of successful cyberattacks begin with a phishing scam?
Types of phishing
The most common types of phishing are:
- Phishing is usually referring to an email message scam.
- Smishing is a text message (SMS) that takes advantage of difficult-to-validate messages and web links on a mobile device.
- Vishing is a bait message on someone’s voicemail asking them to take action and fall for the scam.
- Quishing is a QR code that requires scanning with a cell phone to follow a link.
- Spear phishing can be an email, text or voicemail, where the attacker has done research on the victim with personalized information.
- Tech support scam is typically started by a phone, where the attacker offers help to solve a problem and asks to you use a remote support session to access the device.
Why is phishing a problem for individuals and organizations?
- Prevalence: More than 90% of compromised accounts or hacks start with a phishing attack.
- Speed: More than 60% of victims of a phishing attack “bite” in the first hour, so it is difficult for organizations to react in time to stop the attack.
- Cost: Business email compromise cost organizations $4.1 billion USD in 2020 (up from $1.77 billion in 2019) along with recovery operations and reputational damage.
- Impact: Individuals suffer from phishing, both through workplace shame and cleanup effort, and personal repercussions like identity theft and credit rating damage.